▷The phenomenon of reflection is :
~we can see our own image when we look into a flat mirror.
~The mirror reflects the ray which strikes it.
▷The Laws Of Reflection
~(a) Angle of reflection = Angle of incidence
~(b) The incidence ray,the reflected ray and the normal at the point of incidence are in the same plane.
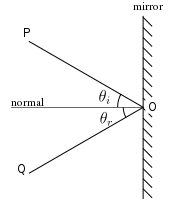
Incident ray : the ray of light which strikes the mirror
Angle Of Incidence : the angle between the incident ray and the normal
Normal : a line which is at right angles to the surface of a mirror
Reflected ray : the ray which reflect back from the mirror
Angle of reflection : the angle between the normal and the reflected ray
▷Application of reflection of light
(a) periscope

~ A periscope is used to view objects above the surface of the sea and used to look at parts of a machine which are otherwise out of our line of vision.
~A simple periscope consists of two mirrors , fixed facing each other at an angle of 45°to the line joining them.
(b)kaleidoscope

~Two plane mirrors inclined at any angle will produce multiple reflections.
~A kaleidoscope uses multiple reflections in plane mirrors which are at 60° to each other.
~The tiny coloured beads inside the kaleidoscope can produces different designs.
▷Types of reflection
(a) regular reflection

~The regular reflection will reflect on the smooth and flat surface.
~All parallel rays will reflected in the same direction.
~The example of regular reflection is mirror.
(b)Irregular reflection
~The irregular reflection will reflect on the rough and matt surface.
~All parallel rays will randomly reflect in different directions.
~The example of irregular is white paper.
▷Reflection of light on a plane mirror
♬ Characteristics of the image formed in a plane mirror :
*laterally inverted
*virtual
*same size as the object
*as far behind the mirror as the object is in front of it
▷Reflection of light on a curve mirror
~concave mirror and convex mirror
♬ characteristics of a images formed by a curve mirror ( concave mirror )
﹝sometimes,the characteristics of a images by a concave mirror must be depends on the distance of a object from the mirror﹞
*relative location
*orientation ( upright / inverted )
*relative size ( magnified / reduced / same size as the object )
*type of images ( real / virtual )
♬ characteristics of a images formed by a curve mirror ( convex mirror )
*virtual
*upright
*smaller than the object
*irrespective of where the object is placed
No comments:
Post a Comment